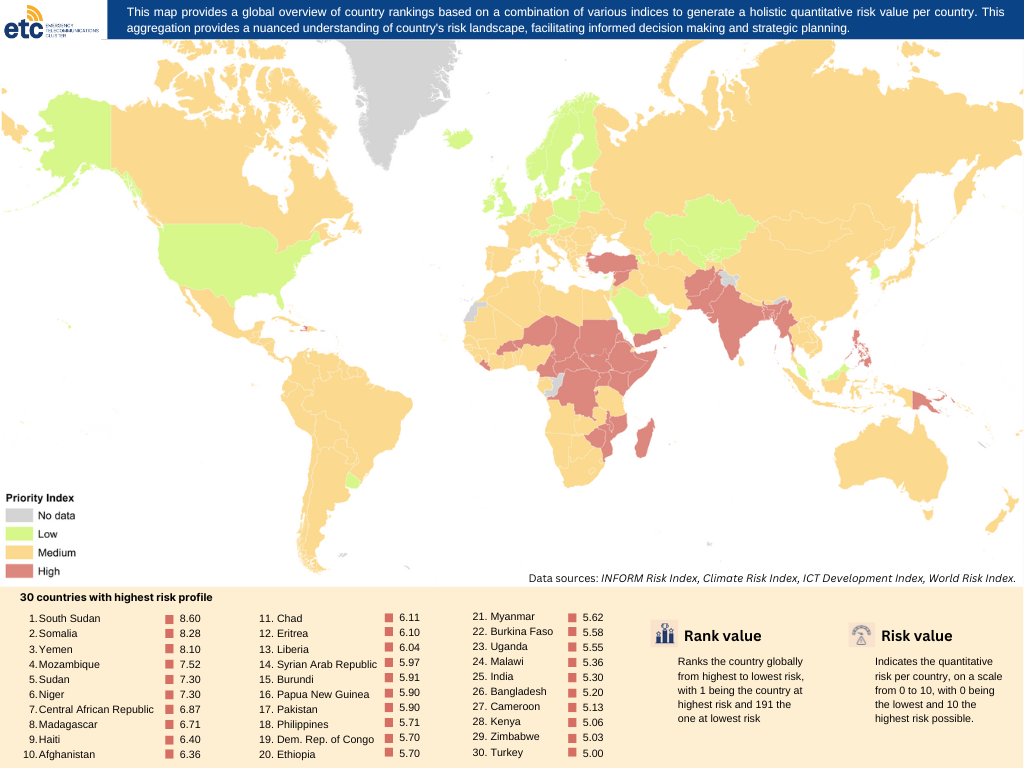
Country Prioritization Methodology
There is an increase in the frequency of disasters across the world and emergency preparedness is a powerful way to mitigate risks and improve the capacity of communities. However, it is not always easy to identify the countries that would most benefit from the assistance of the Global ETC and its preparedness operations, especially when there are countries with multiple disasters and varying hazard types.
The Global ETC has developed a methodology to prioritize those countries most at risk. This model, to be used annually, will entail a thorough analysis of countries at risk as well as their Information and Communications Technology (ICT) capabilities. This list will be used as a tool to inform the judgments regarding local ETC activation, while the ETC supports establishing partnerships with countries which are not included in the final listing. The country prioritization methodology presented in this brief illustrates the considered quantitative and qualitative assessments as well as the weight distribution.
Access the Country Prioritization Methodology.